Remember, total variablecosts change proportionately with changes in total activity, whilefixed costs do not change as activity levels change. These variablemanufacturing costs are usually made up of direct materials,variable manufacturing overhead, and direct labor. The productcosts (or cost of goods sold) would include direct materials,direct labor and overhead.
Components of Absorption Costing
Therefore, as production increases, net income naturally rises, because the fixed-cost portion of the cost of goods sold will decrease. Under variable costing, the fixed overhead is not considered a product cost and would not be assigned to ending inventory. The fixed overhead would have been expensed on the income statement as a period cost. Absorption costing is a very widely used costing system and public entities are bound by GAAP to use absorption costing when reporting their earnings to shareholders. Companies, however, can get information from variable costing and absorption costing systems as long as the companies can calculate the amount of every manufacturing fixed overhead per unit. In summary, absorption costing principles provide businesses with an accurate, GAAP-compliant accounting method to incrementally track product profitability changes tied to production volumes.
Managerial Accounting
While more complex than variable costing, absorption costing gives managers and investors a clearer view of product profitability. In summary, absorption costing provides a comprehensive look at per unit costs by incorporating all expenses related to production. The tradeoff is that net profit fluctuates more than with variable costing methods.
Overhead Absorption Rate Formula
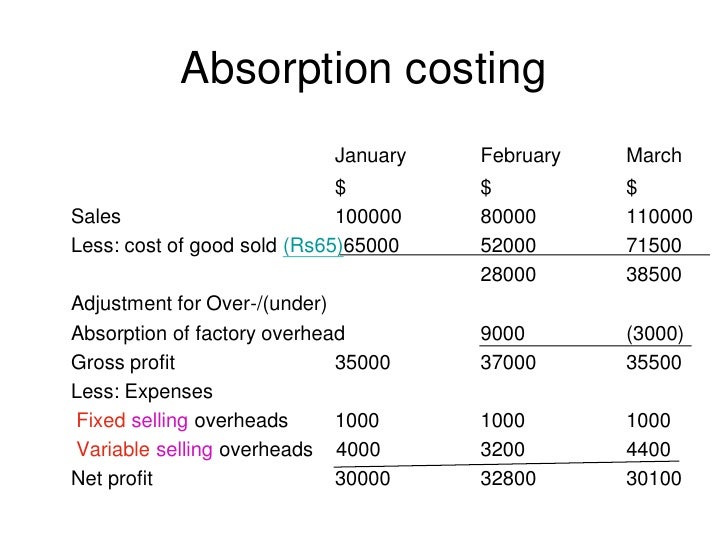
This means that all costs must be included at the end of an inventory, which is normally done as a balance sheet asset. Last but not least, calculate the operating income by subtracting selling and administrative expenses from gross profit. Let’s use the example from the absorption and variable costing post to create this income statement. Absorption costing is not as well understood as variable costing because of its financial statement limitations. But understanding how it can help management make decisions is very important. See the Strategic CFO forum on Absorption Cost Accounting that helps managers understand its uses to learn more.
- Kristin is also the creator of Accounting In Focus, a website for students taking accounting courses.
- As we all know, absorption costing is also known as full cost accounting because, under this method, all of them directly attributable costs of production are included.
- This makes it more difficult for management to make the best decisions for operational efficiency.
- Absorption costing allocates all manufacturing costs, including fixed overhead costs, to the units produced.
This method does not leave out fixed costs like the marginal costing system, instead, all relevant fixed costs are absorbed into the system. Does not meet GAAP requirements – under GAAP product costs are not expensed in the period incurred, they become inventory. The variable cost per unit is 22 (the total of direct material, direct labor, and variable overhead). The absorption cost per unit is the variable cost (?22) plus the per-unit cost of ? By allocating fixed overhead to units produced, absorption costing provides a more complete assessment of production costs. However, it can result in over- or under-costing inventory if production volumes fluctuate.
As with the absorption costing income statement, you begin a marginal costing income statement by calculating gross sales for the period. Next, you calculate variable cost of goods sold and variable selling expenses. To calculate variable cost of goods sold, start with beginning inventory, add variable manufacturing costs and subtract ending inventory. Subtract total variable costs from gross sales to find the contribution margin for the period. Subtract fixed manufacturing overhead and fixed selling and administrative expenses to arrive at net operating income for the period.
In order to complete this statement correctly, make sure you understand product and period costs. Absorption costing fails to provide as good an analysis of cost and volume as variable costing does. If fixed costs are an especially large part of total production costs, it is difficult to determine variations in costs that occur at different production levels. This makes it more difficult for management to make the best decisions for operational efficiency.
If you remember marginal costing, you will remember that we used the sum of marginal variable costs. The different methods of costing used in a manufacturing what is a simple tax return business, result in variations in the format of income statements. Income increases as production increases and decreases as production decreases.
It does not depend on the fact that the unit of the product has been sold or it is still lying in the storage as inventory or finished product ready to be sold. Based on what happens to the product, it will be considered under the inventory calculation or considered under sales revenue and profit calculation. Next, we can use the product cost per unit tocreate the absorption income statement. We will use the UNITS SOLDon the income statement (and not units produced) to determinesales, cost of goods sold and any other variable period costs.

